Corrosive Atmospheres

Corrosive Atmospheres 
Cable ties and their associated fixing devices are generally suitable for use in wet and dry locations and also where subject to exposure to common corrosive elements. While concerns for deterioration resulting from atmospheric corrosion immediately lead one to think of metallic products, some corrosive elements in certain application environments can have equally deteriorating affects on nonmetallic materials. NEMA cable tie Application Bulletin No. 2 addresses the affects of ultra-violet light exposure. Some other types of corrosive environments include: any wet or damp application area; salt laden air as is common in coastal areas; areas known for acid rain; harsh industrial environments; and even areas that are subject to radiation exposure.
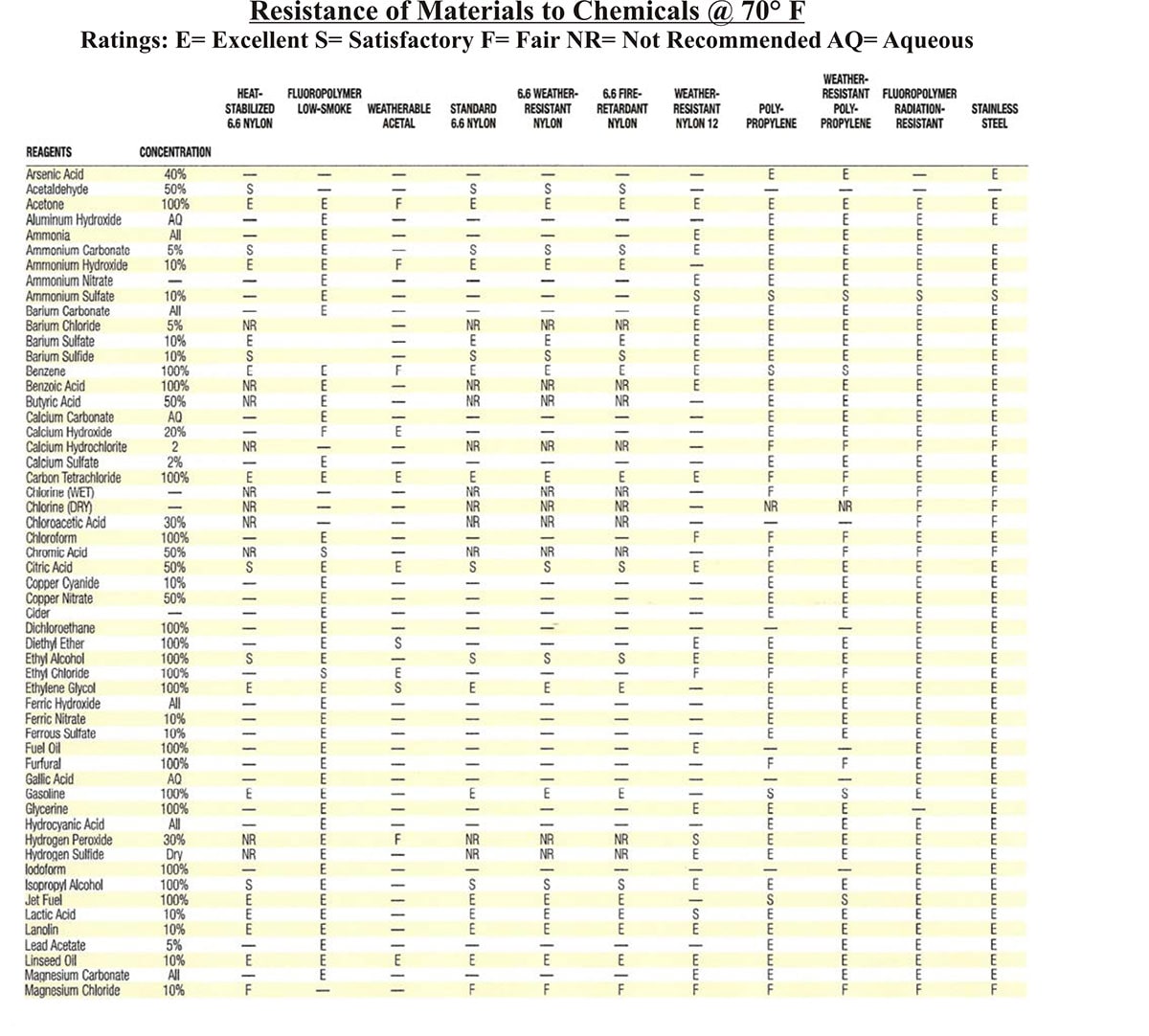
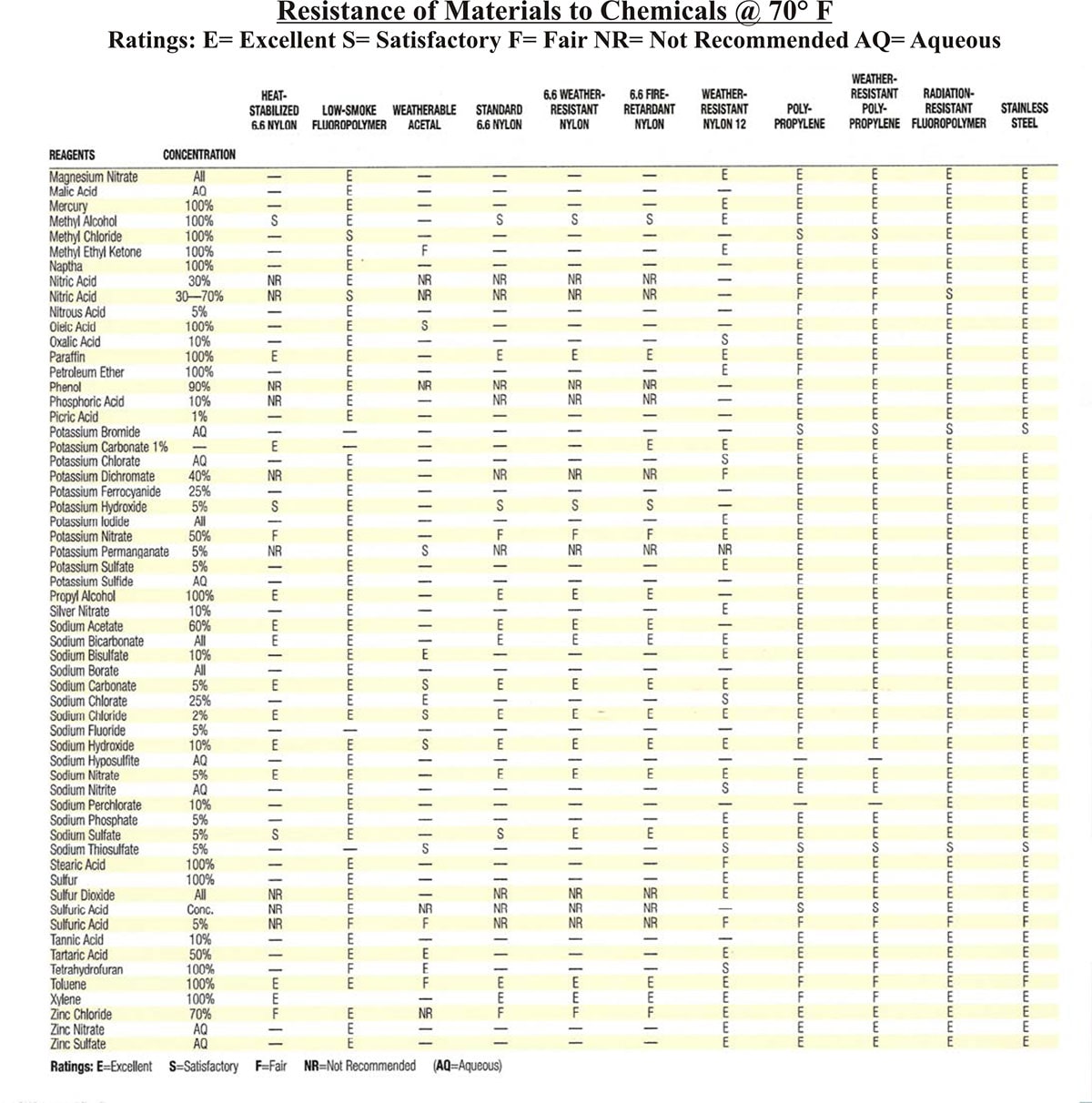
Cable tie products are available in constructions that consist of all metallic materials, composite (combination of metallic and nonmetallic materials), and all nonmetallic materials. Cable ties constructed of the most common nonmetallic materials are generally immune to corrosive affects from exposure to water and moist sodium and sulfur laden atmospheres and are resistant to the affects of many other airborne contaminants. The table below provides guidance on selecting cable tie products constructed from specialized polymer materials where resistance to particular chemicals is a concern.
Products constructed entirely from metallic materials are typically specified where the application places a high reliance on mechanical strength, even when subject to the potential for physical abuse. The National Electrical Code®, NFPA 70, requires all metallic products used in an electrical system to have a degree of resistance to corrosion. Product standards for cable ties include mechanical tests for metallic and composite cable ties and fixing devices both before and after exposure to salt spray. Metallic cable ties as well as metallic components of composite cable ties are most often constructed from stainless steel. Stainless steel grades that contain at least 16% chromium, such as 306, 310 and 316, are generally considered to provide the required minimum degree of resistance to atmospheric corrosion.
The manufacturer should always be consulted if there is a question about the proper application of a cable tie or associated fixing device.
NEMA members provide high value, consistent quality, safe and efficient use for cable ties and their associated fixing devices that meet the expectations of a wide variety of users. Visit us at NEMA Information for Cable Ties for current information on our industry and for the names of NEMA member cable tie manufacturers.
NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
The information in this publication was considered technically sound by the consensus of persons engaged in the development and approval of the document at the time it was developed. Consensus does not necessarily mean that there is unanimous agreement among every person participating in the development of this document.
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) standards and guideline publications, of which the document contained herein is one, are developed through a voluntary consensus standards development process. This process brings together volunteers and/or seeks out the views of persons who have an interest in the topic covered by this publication. While NEMA administers the process and establishes rules to promote fairness in the development of consensus, it does not write the document and it does not independently test, evaluate, or verify the accuracy or completeness of any information or the soundness of any judgments contained in its standards and guideline publications.
NEMA disclaims liability for any personal injury, property, or other damages of any nature whatsoever, whether special, indirect, consequential, or compensatory, directly or indirectly resulting from the publication, use of, application, or reliance on this document. NEMA disclaims and makes no guaranty or warranty, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or completeness of any information published herein, and disclaims and makes no warranty that the information in this document will fulfill any of your particular purposes or needs. NEMA does not undertake to guarantee the performance of any individual manufacturer or seller’s products or services by virtue of this standard or guide.
In publishing and making this document available, NEMA is not undertaking to render professional or other services for or on behalf of any person or entity, nor is NEMA undertaking to perform any duty owed by any person or entity to someone else. Anyone using this document should rely on his or her own independent judgment or, as appropriate, seek the advice of a competent professional in determining the exercise of reasonable care in any given circumstances. Information and other standards on the topic covered by this publication may be available from other sources, which the user may wish to consult for additional views or information not covered by this publication.
NEMA has no power, nor does it undertake to police or enforce compliance with the contents of this document. NEMA does not certify, test, or inspect products, designs, or installations for safety or health purposes. Any certification or other statement of compliance with any health or safety-related information in this document shall not be attributable to NEMA and is solely the responsibility of the certifier or maker of the statement.

 RFQ (
RFQ (